-
[Pytorch] MNIST CNN딥러닝 2020. 3. 31. 01:01
이번에는 MNIST CNN 모델을 만들어보겠습니다. 이번 포스트도
https://adventuresinmachinelearning.com/convolutional-neural-networks-tutorial-in-pytorch/을 참고하였습니다. CNN에 관한 이론은 생략하겠습니다.
Convolutional Neural Networks Tutorial in PyTorch - Adventures in Machine Learning
Learn all about the powerful deep learning method called Convolutional Neural Networks in an easy to understand, step-by-step tutorial. Also learn how to implement these networks using the awesome deep learning framework called PyTorch.
adventuresinmachinelearning.com
CNN 이론에 관련된 좋은 사이트
https://towardsdatascience.com/pytorch-basics-how-to-train-your-neural-net-intro-to-cnn-26a14c2ea29
Pytorch [Basics] — Intro to CNN
This blog post takes you through the different types of CNN operations in PyTorch.
towardsdatascience.com
https://www.youtube.com/watch?list=PLZbbT5o_s2xq7LwI2y8_QtvuXZedL6tQU&v=YRhxdVk_sIs&feature=emb_logo
신경망 구조는 다음과 같습니다
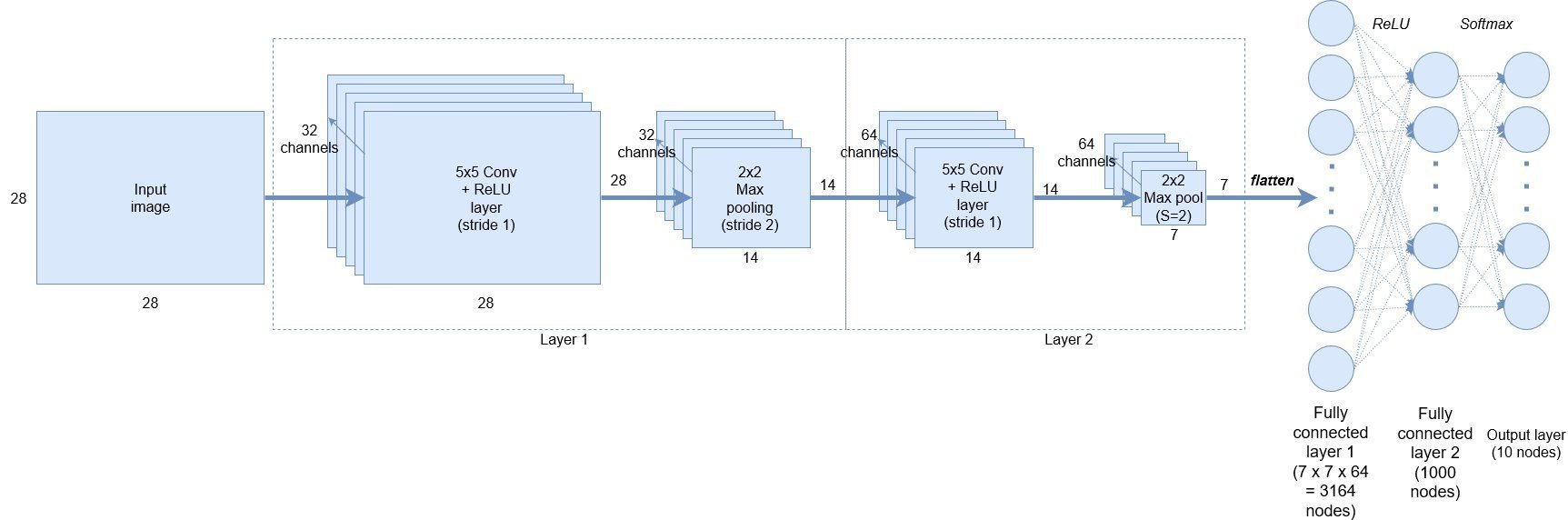
CNN 구조 드에 주석으로 설명하였습니다.
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.optim as optim import torchvision import torchvision.transforms as transfroms import pandas as pd from collections import OrderedDict from IPython.display import clear_outputlearning_rate = 0.001 batch_size = 100 num_classes = 10 epochs = 5train_set = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST( root = './data/FashionMNIST', train = True, download = True, transform = transfroms.Compose([ transfroms.ToTensor() # 데이터를 0에서 255까지 있는 값을 0에서 1사이 값으로 변환 ]) ) test_set = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST( root = './data/FashionMNIST', train = False, download = True, transform = transfroms.Compose([ transfroms.ToTensor() # 데이터를 0에서 255까지 있는 값을 0에서 1사이 값으로 변환 ]) ) train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size) test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=batch_size)class ConvNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.layer1 = nn.Sequential( # 순차적인 레이어 쌓게 함 # Convolution + ReLU + max Pool nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2), # Wout = (Win - FilterSize + 2*Padding)/Stride + 1 nn.ReLU(), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2) ) self.layer2 = nn.Sequential( # 순차적인 레이어 쌓게 함 # Convolution + ReLU + max Pool nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2), nn.ReLU(), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2) ) self.dropout = nn.Dropout() # over-fitting 방지 self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features=7*7*64, out_features=1000) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(in_features=1000, out_features=10) def forward(self, x): x = self.layer1(x) x = self.layer2(x) x = x.reshape(x.size(0), -1) x = self.dropout(x) # 오버피팅을 막기 위해 학습 과정시 일부 뉴런을 생략하는 기능 x = self.fc1(x) x = self.fc2(x) return xDropout에 대해 설명된 사이트
[Part Ⅵ. CNN 핵심 요소 기술] 2. Dropout [1] - 라온피플 머신러닝 아카데미 -
Part I. Machine Learning Part V. Best CNN Architecture Part VII. Semantic ...
blog.naver.com
model = ConvNet() critertion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr = learning_rate)import pandas as pd from collections import OrderedDict from IPython.display import clear_outputtotal_step = len(train_loader) pd_results = [] for epoch in range(epochs): for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader): out = model(images) # 자동으로 forward 함수 불러옴 loss = critertion(out, labels) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() total = labels.size(0) preds = torch.max(out.data, 1)[1] # out은 리스트로 가장 큰 값을 가진 원소의 인덱스가 예측 클래스 # torch.max의 파라미터 중 1은 1차원의 리스트로 출력한다 # 이는 labels이 1차원 리스트로 같게 맞춰주기 위함 correct = (preds==labels).sum().item() # 같은 것은 합해서 맞은 개수 얻음 if (i+1)%100==0: results = OrderedDict() results['epoch'] = epoch+1 results['idx'] = i+1 results['loss'] = loss.item() results['accuracy'] = 100.*correct/total pd_results.append(results) df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(pd_results, orient='columns') clear_output(wait=True) display(df)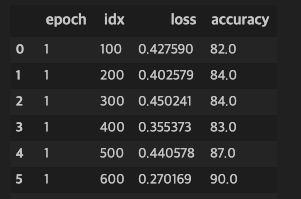
학습 결과 # test model.eval() # evaluate mode로 전환 dropout 이나 batch_normalization 해제 with torch.no_grad(): # grad 해제 correct = 0 total = 0 for images, labels in test_loader: out = model(images) preds = torch.max(out.data, 1)[1] total += len(labels) correct += (preds==labels).sum().item() print('Test Accuracy: ', 100.*correct/total)'딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
[Pytorch] EMNIST CNN (0) 2020.04.03 [Pytorch] MNIST 신경망 구현 (0) 2020.03.28 [Pytorch] 간단한 신경망 구현 (0) 2020.03.16